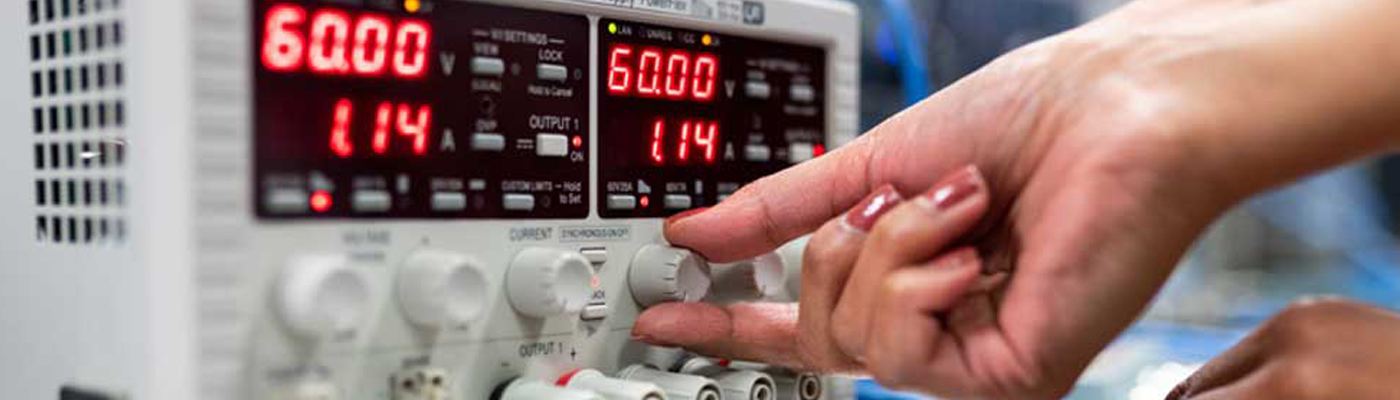
Calibrations
We calibrate all major brands of test equipment, to current industry standards, with a team who know and understand that you require your Test Instruments asap, giving unequalled turnaround times. Fully traceable to international standards and a full calibration certification, giving you the peace of mind that your tester meets the current legislation.
UK National standards
Our calibration procedures provide line by line traceability to UK National standards. Results, parameters and uncertainties are recorded on all certificates. Calibration is carried out with National Laboratory and UKAS traceable equipment
Swindon and Wiltshire Calibrations
As we are a Swindon based Calibration company, we can offer you a same day and cheaper Calibrations of your PAT Testers, Multi Function Testers and more. Based in Swindon, you can drop your tester off and be ready to pick up or we can deliver back to you in quick time.


Calibration is an essential process in many industries and applications where accurate measurements are required. The process of calibration involves comparing an instrument or device to a standard and making any necessary adjustments to ensure the instrument is measuring accurately. This article will explore the key concepts and terms related to calibration, including standardization, verification, and validation, as well as the importance of traceability, accuracy, and precision in measurement.
Standardisation is the process of establishing and maintaining uniform standards for measurement. This is important because it ensures that measurements made with different instruments or devices are comparable and can be used together in a consistent manner.
Verification involves comparing an instrument or device to a standard to determine its accuracy. This is typically done before the instrument is put into use, and is repeated at regular intervals to ensure the instrument continues to perform accurately.
Validation, on the other hand, is the process of ensuring that an instrument or device meets specific requirements for accuracy and precision. This is usually done in a laboratory setting and may involve multiple tests and measurements to ensure that the instrument is performing as expected.
Traceability is the ability to trace the measurement made by an instrument back to a known standard. This is important because it provides a means of checking the accuracy of the measurement, and it also helps to ensure that the measurement is consistent and comparable over time.
Accuracy and precision are two important concepts in calibration. Accuracy refers to the degree to which a measurement is close to the true value, while precision refers to the reproducibility of the measurement. Both accuracy and precision are important for ensuring that measurements are reliable and useful.
Instrumentation is a critical component of calibration. The accuracy of the measurement depends on the performance of the instrument, so it is important to choose instruments that are capable of making accurate measurements.
Metrology is the science of measurement, and it is concerned with the development and application of methods for making accurate measurements. Metrologists work to develop and maintain the standards used for calibration, and they also develop new techniques for making measurements.
Reference standards are the standards used for calibration. These standards are usually maintained by a national metrology institute and are used to check the accuracy of instruments and devices.
Adjustment is the process of making changes to an instrument to improve its accuracy. This may involve adjusting the instrument's sensitivity, or making changes to its design to improve its performance.
Alignment is the process of ensuring that an instrument is properly aligned with a standard. This is important because even small misalignments can result in significant measurement errors.
Linearity, repeatability, and stability are three important concepts in calibration. Linearity refers to the relationship between the output of an instrument and the value being measured. Repeatability refers to the ability of an instrument to make the same measurement repeatedly, while stability refers to the ability of an instrument to maintain its accuracy over time.
Tolerance is a measure of the acceptable deviation from a standard. This is important because it sets the limits for what is considered acceptable performance for an instrument.
Calibration intervals are the intervals at which an instrument is calibrated. These intervals are determined based on the performance of the instrument and the requirements for accuracy and precision.
A calibration certificate is a document that provides evidence of an instrument's calibration. This certificate is usually issued by a calibration laboratory and it provides information about the instrument's performance, including its accuracy and precision.
Calibration laboratories are facilities that are equipped and staffed to perform calibrations. These laboratories usually have a range of standards and instruments, as well as the expertise required to perform calibrations accurately.
Calibration management systems are systems that are used to manage the calibration process.
